详细介绍
#关键词:弹性体缓冲器 防撞缓冲器 特殊环境缓冲器 交通安全 日常生活
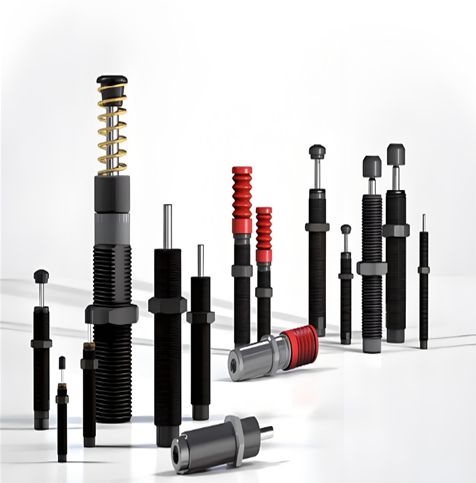
Classification of buffers
Buffer also plays an important role in transportation, daily life, and special scenarios. The demand for buffers in these scenarios focuses more on safety, comfort, and special environmental adaptability, which has led to various types of buffers such as elastic buffers, anti-collision buffers, and special environmental buffers. They are designed with unique structures to meet the buffering needs in different scenarios and provide guarantees for people's travel and life.
Elastic buffer is made of elastic materials such as rubber, polyurethane, silicone, etc. It relies on the elastic deformation of the material itself to absorb impact energy, and has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, and good sound insulation effect. It is the most widely used type of buffer in daily life and lightweight equipment. Rubber buffer is a representative of it, with good elasticity and wear resistance. It can be made into various forms such as sealing rings and buffer pads, and is used in automotive shock absorption systems, household appliance bases, door and window sealing strips, and other scenarios. In the suspension system of automobiles, rubber buffer blocks can effectively absorb the impact generated by road bumps, reduce the transmission of vibration to the body, and improve ride comfort; In household appliances, rubber cushioning pads can reduce vibration and noise during device operation, avoiding damage caused by collisions between the device and the desktop.
The polyurethane buffer is superior to the traditional rubber buffer in performance. It has higher hardness, wear resistance and aging resistance, and can maintain stable performance in a wide temperature range. Therefore, it is used for shock absorption of heavy trucks, buffer parts of construction machinery and other scenarios. Silicone buffers, with their high temperature resistance and chemical corrosion resistance, are suitable for fields with high environmental requirements such as kitchen appliances and medical equipment, such as microwave door buffer sealing and surgical instrument protection buffer. Their environmentally friendly and non-toxic characteristics also make them widely used in food processing equipment.
Anti collision buffer is a core safety component in the field of transportation, mainly used to absorb the huge energy generated during vehicle collisions, protect the safety of vehicle drivers, passengers and road facilities. According to application scenarios, it can be divided into two categories: vehicle collision buffer and road collision buffer. Vehicle collision buffers are installed at the front and rear ends of vehicles such as cars and trains. For example, the bumper buffer structure of a car usually uses a combination of energy absorbing boxes and elastic bodies inside. When a minor collision occurs, the elastic body absorbs energy to avoid damage to the vehicle body; When a serious collision occurs, the energy absorbing box undergoes plastic deformation, further absorbing the impact energy and reducing the damage to the driver and passengers caused by the collision. The collision buffer at the connection of train carriages is more complex, combining the dual advantages of mechanical and hydraulic buffers, which can effectively cope with the huge impact force generated during train start stop and emergency braking.
Road collision buffers are installed on dangerous road sections such as highway guardrails, bridge piers, tunnel entrances, etc. They usually adopt modular design and consist of buffer plates, energy absorbing modules, brackets, etc. When the vehicle loses control and collides, the buffer plate transfers the impact force to the energy absorbing module. The energy absorbing module absorbs energy through its own compression, fragmentation, and other methods, gradually reducing the vehicle speed and avoiding serious accidents caused by direct collision with rigid facilities. In recent years, with the increasing awareness of traffic safety, the application scope of road collision buffers has continued to expand, and their materials have gradually developed from traditional metal structures to composite materials to achieve lighter weight and higher energy absorption efficiency.
Special environment buffer is a specialized buffer device designed to adapt to extreme environments such as high temperature, high pressure, strong corrosion, flammability, and explosiveness. It is indispensable in fields such as petrochemicals, aerospace, and mining. For example, buffers in the aerospace industry need to work in high-altitude, low-temperature, and high-speed impact environments. They are usually made of high-strength materials such as titanium alloys, combined with a dual structure of hydraulic and mechanical buffers to ensure smooth buffering during spacecraft landing or component separation; The buffer in the petrochemical industry needs to have strong corrosion resistance, using stainless steel material and a special sealing structure to prevent medium leakage and achieve impact absorption during equipment operation.
These different types of buffers, from the subtle aspects of daily life to the core processes of industrial production, and even to extreme environments in special fields, are all safeguarding safety and stability with their unique performance. With the development of materials science and manufacturing technology, the classification of buffers will continue to be refined, and their performance will be further improved, providing more reliable buffering guarantees for more scenarios.