详细介绍
How to detect the quality of flame detectors: signal analysis and processing detection
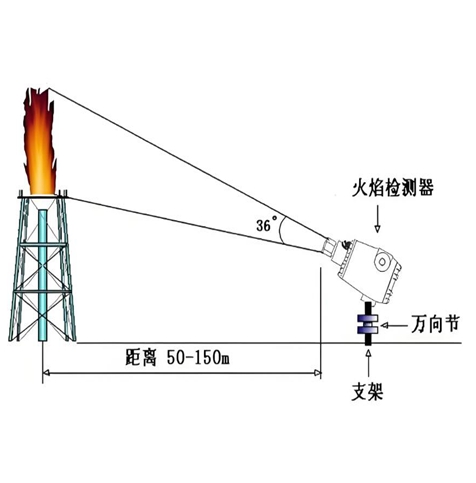
The working principle of a flame detector is to convert the detected flame signal into an electrical signal or other recognizable signal, and process and transmit it. Therefore, the analysis, processing, and detection of signals are one of the core contents for judging the quality of flame detectors.
Firstly, check whether the signal output type and format of the flame detector comply with the standards. Different types of flame detectors may output different types of signals, such as analog signals, digital signals, etc. For analog signals, it is necessary to check whether the voltage or current range is within the specified interval. For example, a common analog signal output may be a 4-20mA current signal. If the actual output signal exceeds this range, it indicates that there is a problem with the detector's signal output. For digital signals, it is necessary to check whether the encoding format is correct, whether the data transmission is stable, and whether there is any packet loss or erroneous data.
Next, analyze the stability of the signal. In the case of stable flame combustion, the signal output by the flame detector should be relatively stable. Use professional signal detection equipment, such as oscilloscopes, to monitor the output signal of the detector in real-time. Observe whether the waveform of the signal is stable and whether there are obvious fluctuations or interference. If the signal waveform frequently fluctuates up and down, or is mixed with irregular clutter, it indicates that the signal has been interfered with, which may be due to problems with the internal circuit of the detector or the influence of the surrounding electromagnetic environment. At this point, it is necessary to further investigate the interference source and check the anti-interference performance of the detector.
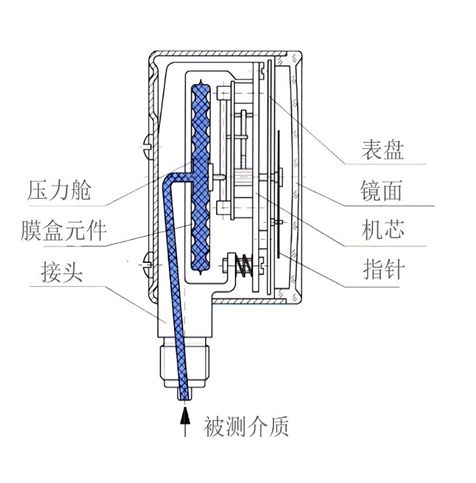
Then, test the signal processing function. Flame detectors usually perform certain processing on the detected signals, such as amplification, filtering, shaping, etc. Check if these processing functions are working properly. For example, by inputting a standard flame signal of known intensity, observe the changes in the detector output signal. If the signal is not amplified as expected after processing, or if the filtering effect is poor and there is still a lot of noise, it indicates that there is a fault in the signal processing part.
In addition, it is necessary to test the signal transmission function of the flame detector. Connect the detector to the control system, simulate actual working scenarios, and test the accuracy and reliability of signals during transmission. Check whether the signal can be transmitted completely and accurately to the control system, and whether there is any signal loss or delay. If there is a problem with signal transmission, it will affect the control system's judgment and control of the flame state, thereby threatening the safe operation of the entire combustion system.
#Flame detector, signal analysis, signal processing